X-Ray Nondestructive Inspection Systems
TXMotion series of high-speed X-ray fluoroscopic inspection systems
Visualization of the inside of a product during high-speed movement

| Applications | ・Internal observation of dropped precision devices ・Analysis of the damage process of electric and electronic components ・Observation of the movement of mechanical and moving components ・Observation of the movement of fluids and granular materials, welding phenomena, etc. |
|---|
TXMotion is capable of capturing moving images at frame rates of up to roughly 20,000 frames per second. It is suitable for recording the internal movement of fast-moving objects that cannot be captured with conventional X-ray fluoroscopic inspection systems.
FEATURES
Visualization of high-speed internal product behavior
With TXMotion, you can view the high-speed internal behavior of objects that cannot be observed with conventional X-ray fluoroscopic inspection systems.
TXMotion can capture moving images at frame rates of up to roughly 20,000 frames per second (depending on imaging conditions).
The maximum imaging area is φ200 mm.
TXMotion can be tailored to suit any customer requirements, including:
・Combination with a micro-CT system
・Combination with vibration, temperature, and other environmental testing systems
・Synchronous operation of multiple cameras to capture external and X-ray fluoroscopic images simultaneously

CASE EXAMPLE
Freefalling TV remote controller
The following video shows how the battery electrodes bounce off the terminals in the battery compartment.
This video is recorded at 5,000 fps (i.e., at a capture interval of 200 μs).
・The left-hand battery is detached from the terminal for roughly 1 ms
・The right-hand battery is detached from the terminal for roughly 3 ms
Application example for the high-speed X-ray fluoroscopic inspection system
In the following example, X-ray generators and X-ray image intensifiers are attached to the robot respectively.
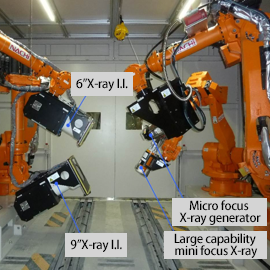
Courtesy: Joining and Welding Research Institute Osaka University